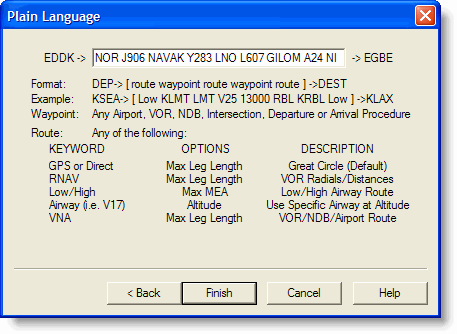
The plain language option takes direct input of waypoints and routing. Pilots often know exactly what clearances ATC will give them for certain routes. Since this may not be the most efficient in terms of distance or aircraft performance, FliteStar probably would not develop the same route.
Plain language is available only for routes with no fuel stops or must/fly points, and you must follow the syntax shown below.

To create a direct route or specify direct routing from one waypoint to another, enter the waypoints in order separated by a space. If you are accustomed to entering specific terminology between each waypoint to designate a direct route, you can enter DCT, GPS or LORAN between the waypoints. The following example shows the same route using different direct route formats:
KPDC LKV LOW KLAS VNA AMBRR AMBRR.BLH4 KPHX
KPDC DIRECT LKV LOW KLAS VNA AMBRR AMBRR.BLH4 KPHX
KPDC GPS LKV LOW KLAS VNA AMBRR AMBRR.BLH4 KPHX
KPDC DCT LKV LOW KLAS VNA AMBRR AMBRR.BLH4 KPHX
Direct routes follow the shortest path from one waypoint to another with no intermediate stops. For direct routing, ensure your altitude clearances are appropriate by viewing the Profile View after the route is created.
Enter VNA between two waypoints to generate a route with VORs, NDBs, and airports as navigation points. For VNA routing, ensure your altitude clearances are appropriate by viewing the Profile View after the route is created.
After specifying VNA or any of the direct routing key words in the route line, you can enter an optional maximum leg length between waypoints. For example, enter a VNA route from KOGD to KAMA with a maximum leg length of 75 miles as KOGD VNA 75 KAMA.
Entering LOW or HIGH between waypoints auto-routes through the high or low altitude airway network. When entering LOW or HIGH, be sure to include an entry waypoint and an exit waypoint. Entry and exit waypoints can be the departure and destination airport, VORs, or enroute airspace fixes connected to an airway. When routing through the high and low network, the altitude on the route is set higher than the minimum altitude required for obstacle and terrain clearance.
After specifying LOW or HIGH in the route line, you can enter an optional maximum MEA. FliteStar will not plan a route where the MEA is higher than what you specified. For example, here is a route entry from one airport to another using low airway routing with a maximum MEA of FL190: KPDX LOW FL190 KSLC.
You can enter an airway route by using any two waypoints in the airway, separated by the airway designator (e.g. V23, J14). If the airway is not connected to the specified waypoints, the route will not work. When using an airway in plain language routing, you must specify entry and exit waypoints. If you change from one airway to another, the transition point is also required.
When choosing an airway, first select a VOR/Airport/Airspace fix that connects to the airway. For example, looking at Lamar Municipal Airport ( KLAA), there are several airways that can be taken from this departure. Traveling to Meade Municiple (KMEJ), V10 is chosen, but V10 does not include KMEJ; another airway is needed. Between the airways, the transition waypoint connecting the airways must be specified.
Plain Language entered: KLAA -> LAA V10 GCK V17 FLACK -> KMEJ
If a departure or destination airport has a SID/STAR you would like to use, enter the procedure name and transition using the following formats:
For SIDs, the format is entered as departure name.transition.
For STARs, the format is entered as transition.arrival name.
Example: KTVL -> RICHY5.MARRI V165 FMG V6 SAC.PYE1 -> KSFO
Leaving off the transition (.) brings up an error about the procedure name not being found as a waypoint.
You only can add pilot-nav SIDs and STARs to your FliteStar route. A pilot-nav SID, as opposed to a vector SID, is one that specifies waypoints and altitudes as part of the procedure.
If you are entering VNA, LOW, or HIGH airway routing before going into a STAR, you need to identify an exit waypoint. This is easily recognized by the STAR because they are usually named according to the point at which the procedure begins. To enter or modify a procedure after the route is created, see Adding or Removing SIDs/STARs.
When typing a waypoint, the following codes allow you to specify what type of navaid you want. For example, if you want airport ABC, you would enter the waypoint as A;ABC.
|
Navaid |
Code |
|
Airport |
A |
|
Intersection |
I |
|
NDB |
N |
|
Route Segment |
R |
|
User-defined Waypoint |
U |
|
VOR |
V |
You can enter a waypoint that is not in the Jeppesen database by typing in a latitude and longitude. Enter degrees, minutes, and decimal minutes in the format of Nddmm.hhWdddmm.hh where:
N = North (N) or South (S)
W = West (W) or East (E)
dd and ddd = degrees. Pad with leading zeros so there are always two digits for latitude and three digits for longitude.
mm = Optional, pad with a leading zero so you always have two digits. Minutes.
hh = Optional. Hundredths of minutes. Enter only one digit for tenths.
The following are some examples:
N45W122 — North 45 degrees, West 122 degrees.
S05E007 — South 5 degrees, East 7 degrees. You must use leading zeros if latitude degrees are only one digit, or longitude is less than three digits.
N4504W12206 — North 45 degrees, 4 minutes. West 122 degrees, 6 minutes.
S4504.2E02206.5 — South 45 degrees, 4.2 minutes, East 22 degrees, 6.5 minutes.
S4504.23E02206.63 — South 45 degrees, 4.23 minutes, East 22 degrees, 6.63 minutes. You can enter hundredths of minutes if desired. Just add a second digit after the decimal point.